Volume 5 | Issue 1 | 2024
Editorial
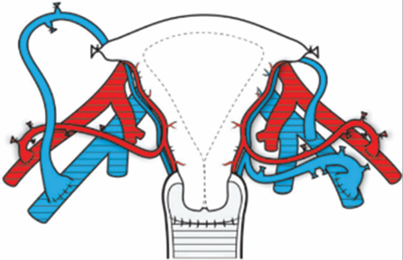
A Life Giver and Life Enhancing Transplant – Uterus Transplant
[Shilpa Nitin Chaudhari]
Case Reports
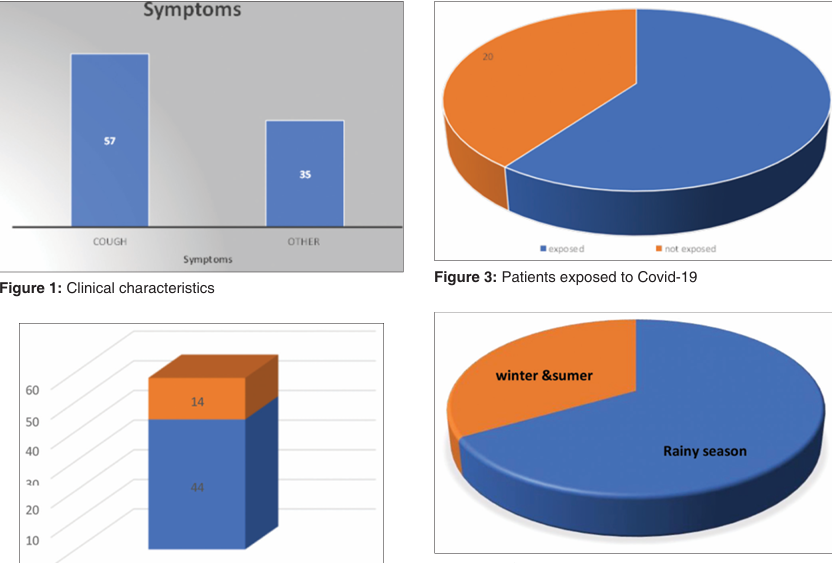
Clinical Features and Outcome of Severe Acute Respiratory Infections during Covid-19 Pandemic 2020 to 2021 in Tertiary Care Hospital
[Ajit B. Bhandarge, Sanjay Natu, Sameer Mhatre, Tushar Deshpande]
View as PDF | HTML
Abstract
Immunocompromised (IC) populations are at increased risk of vaccine-preventable diseases (VPDs). In India, the concern
of VPDs in IC populations is particularly acute due to the prevalence of crowded living situations, poor sanitation, and
variable access to healthcare services. We present a narrative review of IC-related disease and economic burden, risk of
VPDs, and vaccination guidelines, based on global and India-specific literature (2000–2022). IC conditions considered were
cancer, diabetes mellitus, chronic kidney disease, respiratory disorders, disorders treated with immunosuppressive therapy,
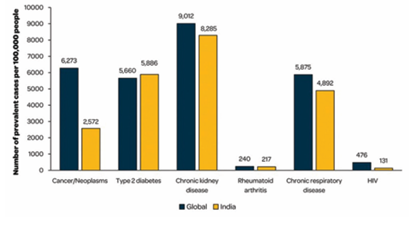
and human immunodeficiency virus (HIV). The burden of IC populations in India is comparable to the global population,
except for cancer and HIV, which have lower prevalence compared with the global average. Regional and socioeconomic
inequalities exist in IC prevalence; VPDs add to the burden of IC conditions, especially in lower-income strata. Adult
vaccination programs could improve health and reduce the economic impact of VPDs in IC populations.
Keywords: Immunocompromised (IC), vaccine-preventable diseases (VPDs), human immunodeficiency virus (HIV)
Adult Vaccination: Unmet Needs and Public Health Implications
[ Ajinkya Pawar, Mukund Saraf, Saurabh Padole, Jitendra Ingole]
View as PDF | HTML
Abstract
Immunocompromised (IC) populations are at increased risk of vaccine-preventable diseases (VPDs). In India, the concern
of VPDs in IC populations is particularly acute due to the prevalence of crowded living situations, poor sanitation, and
variable access to healthcare services. We present a narrative review of IC-related disease and economic burden, risk of
VPDs, and vaccination guidelines, based on global and India-specific literature (2000–2022). IC conditions considered were
cancer, diabetes mellitus, chronic kidney disease, respiratory disorders, disorders treated with immunosuppressive therapy,
and human immunodeficiency virus (HIV). The burden of IC populations in India is comparable to the global population,
except for cancer and HIV, which have lower prevalence compared with the global average. Regional and socioeconomic
inequalities exist in IC prevalence; VPDs add to the burden of IC conditions, especially in lower-income strata. Adult
vaccination programs could improve health and reduce the economic impact of VPDs in IC populations.
Keywords: Immunocompromised (IC), vaccine-preventable diseases (VPDs), human immunodeficiency virus (HIV)
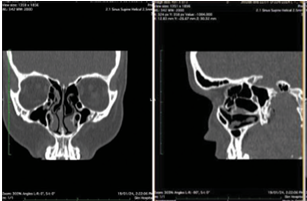
Case Series on Anatomical Variants of Paranasal Sinuses on Computed Tomography
[Piyush Srivastava, Pooja Shah]
View As PDF | HTML
Abstract
A comprehensive understanding of paranasal sinus anatomy is crucial for clinicians. Traditional radiological techniques fall
short in detailing the nasal cavity and paranasal sinuses, which are now better visualized through computed tomography (CT)
imaging. CT provides detailed anatomical perspectives and identifies common anatomical variants. Recognizing these variants is
essential for the safe application of modern endoscopic sinus surgery, as it helps avoid potential complications. Multidetector CT
is increasingly used to image the paranasal sinuses before functional endoscopic sinus surgery. Multiplanar imaging, particularly
coronal reformations, offers accurate insights into sinus anatomy and its variations, which is vital before surgical procedures.
This study focuses on anatomical variants in the nasal fossae and paranasal sinuses observed through CT and highlights several
common anatomical variations, excluding broader anatomical variations such as deviated nasal septum and concha bullosa.
Keywords: Anatomic variants, computed tomography, functional endoscopic sinus surgery, paranasal sinuses, sinusitis
subject – radiology
Correlation of Liver Function Test and Serum Bile Acid with Feto-Maternal Outcome in
Patients with Intrahepatic Cholestasis of Pregnancy – Case Series
[Sharvari Pote, Shilpa Nitin Chaudhari]
View As PDF | HTML
Abstract
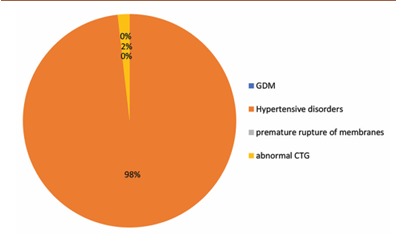
Background: The incidence of intrahepatic cholestasis of pregnancy (IHCP) in India is 0.02–2.4% IHCP is the foremost liver disorder, presenting substantial risks and complications to maternal and fetal health. Characterized by pruritus and elevated bile acids and serum transaminases. Materials and Methods: The study focuses on profiling 6 patients of ICP understanding the correlations between liver function tests with serum bile acid and evaluating the impact of ursodeoxycholic acid (UDCA) treatment and also focus on various maternal and fetal outcome. Results: The study identified a predominance of primigravida (83%) of 26–30 years of age (66%), with maximum patients with moderate serum bile acid levels. IHCP diagnosis was commonly noted between 32 and 36.6 weeks GA (66.6%). The treatment with UDCA 300-BD (in 66% of patients) was providing relief to about 66% of participants within a week. Most deliveries occurred between 37 and 39 weeks GA, predominantly through vaginal Deleveries (83%). Post-partum hemorrhage was seen in 33% of patients. Fetal outcomes revealed a 66% incidence of meconium-stained liquor and about 33% neonatal intensive care unit admissions with no fetal mortality. Most participants (83%) had serum bile acid levels in the 10–40 μmoL/L range. Conclusion: Significant correlations were noted between serum glutamate oxaloacetate transaminase and serum glutamate pyruvate transaminase and with alkaline phosphatase and bile acid. In contrast,
bilirubin showed no significant correlations. Higher UDCA dosages showed a dose-response relationship, implying their effectiveness in managing ICP.
Keywords: Intrahepatic cholestasis of pregnancy, serum bile acid, serum glutamate oxaloacetate transaminase, serum
glutamate pyruvate transaminase, ursodeoxycholic acid
A Case of Glanzmann Thrombasthenia
[ Anvita Jain, Sanjay Natu]
View As PDF | HTML
Abstract
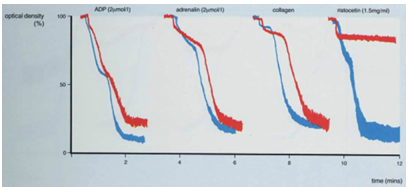
Glanzmann thrombasthenia (GT) is a rare congenital autosomal recessive platelet function disorder characterized by defective
platelet aggregation due to abnormalities in the glycoprotein IIb/IIIa complex. Clinically, it presents with mucocutaneous
bleeding, including epistaxis, gingival bleeding, and easy bruising.
Keywords: Glanzmann thrombasthenia, epistaxis and gingival
Case of a Floppy Infant: Contiguous Gene Syndrome
[ Monica Chand, Sanjay Natu]
View As PDF | HTML
Abstract
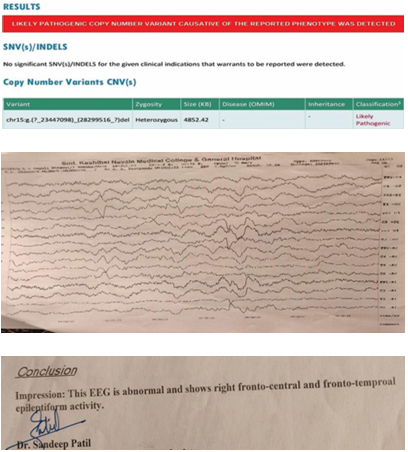
Case of a 29-day-old male baby having hypotonia and respiratory distress, which on further evaluation came to be diagnosed
as contiguous gene syndrome (15q11–13 gene deletion).
Keywords: Hypotonia, malformations, genetic or metabolic disorders
Orofacial Granulomatosis Masquerading as Borderline Tuberculoid Leprosy – A Rare
Case Report
[Sanchita Singhal, Nitin Chaudhari, Swapna Sheth]
View As PDF | HTML
Abstract
Orofacial granulomatous disease is characterized by non-necrotizing granulomatous inflammation of the oral and
maxillofacial region. Clinical findings include labial inflammation, perioral and mucosal inflammation, mouth ulcers,
and gingivitis. Leprosy is a chronic, granulomatous, and multisystem disease and the involvement of lips is an extremely
rare entity that can be mistaken for a variety of other granulomatous conditions. Hence, histopathological examination is
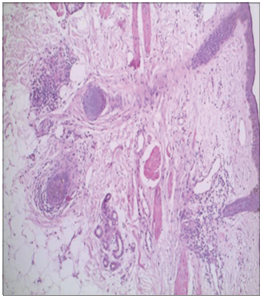
necessary in such a case scenario to overcome the challenges that a professional has to face. Herein, we report a patient who
presented with chronic asymptomatic swelling of the left cheek and upper lip which was later histopathologically confirmed
to be a case of orofacial granulomatosis.
Keywords: Orofacial granulomatosis, Crohn’s disease and sarcoidosis
